This Post will explain , how to Deploy Spring Boot Application on Pivotal Cloud Foundry Platform
Now a days Cloud Computing and Microservice have become very popular concept and almost all the organizations are investing and adapting it very fast. Currently there are only
few popular cloud providers in the market and Pivotal Cloud Foundry is one of them. It is a PaaS(Platform AS A Servcie) service where we can easily deploy and manage our
applications and the Cloud Foundry will take care of the rest of the cloud based offerings like scalability, high availability etc.
Today we will learn to deploy spring boot application in Pivotal cloud foundry platform called as Pivotal Web Services.
Step 1: What is Cloud Foundry?
Cloud Foundry is an open-source platform as a service (PaaS) that provides you with a choice of clouds, developer frameworks, and application services. It is open source and it is governed by the Cloud Foundry Foundation. The original Cloud Foundry was developed by VMware and currently it is managed by Pivotal
Step 2: Now we need to install Cloud Foundary on Windows
Step 3: Download Cloud Foundary Windows Installer using this link
Step 4: Unzip the file, From the place where you have saved the downloaded file.
Step 5: Double Click on the cf_installer.exe file and click on the next.. next buttons until it completes

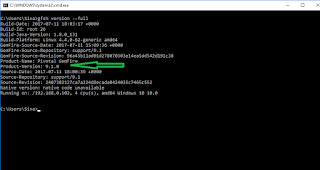
Step 6: If you have successfully installed then you can check the CLI version or other details
Enter cf command prompt. It will give list of options which cf will accept.
c:/> cf vesion - will give full CLI version details
Step 7: Now we need to be setup Pivotal Webservice Console (PWS)
Step 8: Provide necessary details and sign up the same.

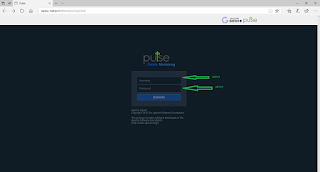
Once sign up is completed, we can log into the Pivotal webservice console through the login screen of the pivotal web service console.
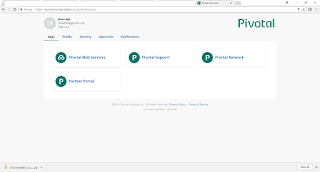
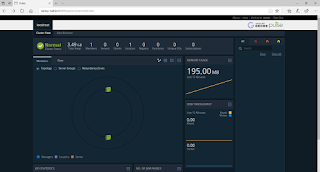
After providing login credentials successfully we will get into the cloud foundry console where we can see all the deployed applications, can monitor the applications and do many more activities. Here we need to add org and space etc...
Step 9: Once we have created org and space successfully.. now we need to deploy the spring boot application in PCF.
Step 10: Before that , Login in to PWS (Pivotal Webservice Console) using CLI
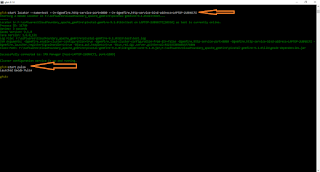
c:/> cf login -a api.run.pivotal.io
Provide username and password which is given , while registering the PWS.
same way we can use Logout
c:/> cf logout
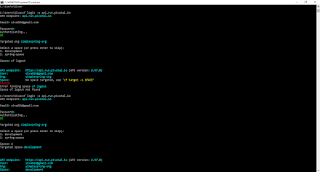
Step 11: Now login and logout is working with out any issues.
Step 12: Now write simple spring boot application and run the same in locally.
If you want to write simple one follow the https://start.spring.io/ - which will create sample spring boot application for you and modify as per your requirment.
i have created one sample arthimetic operations spring boot application.. check in
my previous post for the same.
add the below code into bootstrap.properties under src\main\resources
server.contextPath = /
management.security.enabled = false
Step 13: Once we have completed the Spring boot application and executed successfully in local environment.
Now we need to push the same into Pivotal cloud Foundary.
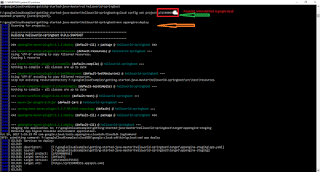
Step 14: login into PWS using CLI c:/> cf login -a api.run.pivotal.io
Step 15: Go to where spring boot application is saved . Then push to PCF
F:\spring_boot_example\helloworld-springboot>cf push helloworld-springboot -p target\helloworld-springboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar



Step 16: Now we have deployed spring boot application into Pivotal Cloud Foundary Successfully.
Step 17: Open the PWS console and check the details. whether pushed application through CLI is available or not in PWS console.

Step 18: Open the below links and you can see the output as follows.
https://helloworld-springboot.cfapps.io/
https://helloworld-springboot.cfapps.io/add/20/30
https://helloworld-springboot.cfapps.io/substract/20/30
https://helloworld-springboot.cfapps.io/multiply/20/30
https://helloworld-springboot.cfapps.io/division/20/30

Step 19: This is how we will implement spring boot application and we can deploy the same in Pivotal Cloud Foundary.
Thank you very much for viewing this post. if you like this please share the same
If you face any issues.. write a comment and you will get reply the same