This post will explain you about spark built in libraries
Libraries
-
SQL – processing semi structured data , using the structured query to optimize the data
-
Streaming- it is officially described enabling the processing live streams of the data
in scalable,fault tolerant manner.
The ability to switch between batch analysis and writing the streaming
-
MLlib/GraphX-
MLlib is used to machine learning more scalable and easy
-
GraphX is more on data parallel and Graph parallel computation
Spark SQL
1. It works with the data with similar fashion with SQL
2. It goal is to meet SQL-92 standards
myStructureData.registerTempTable(“SparkTable)
sqlContext.sql(“select * from SparkTable where SomeColumn==’someData’”)
3. But we can write the creative code let the engine use as much of data and storage structure as much as it can to optimize the result and distributed query behind the scene.
4. The main goal is developer not worry about distributed nature as much and focus on your business usecases.
5. As Spark continues to grow ,we want to enabler wider audiences beyond Big Data engineers to leverage the power of distributed processing
How we will compare Spark SQL with other competitors?
1. Apache Hive
- It very slow and require complex custom user defined functions.
- Simply to extends it’s functionality
- Unit testing is very difficult.
- If we are having already hive then we have mechanisms to use existing hive table structure into Spark SQL
- If we use Spark SQL it is 100 times faster when compare to Hive
2. Apache DRILL
- It is very new and focusing on the sql on Hadoop
3. Impala
- It is C++ established tool and it can beats spark in direct performance benchmark
4. Spark can work with many data sources.
Data Sources
1. Hive
- Spark SQL originated from product called shark
- Shark is very much hive on Spark and it is quite successful
- It is re written in decoupling the code and keeping the best parts and known as Spark SQL
- If want to Couple with Hive, then we need to copy hive-sev.xml file into spark home conf directory
- After this we will have automatically access to the hive administrator.
- Even it supports Hive UDF’s
- If we want to access existing table just load it by name.
2. JSON
3. Parquet
4. Avro
5. Amazon REDSHIFT
6. CSV
1. Optimizations
a. Predicate push down
b. Column pruning
2. Uniform API
3. Code generation == Performance gains
1. Optimizations
a. Predicate push down
b. Column pruning
2. Uniform API
3. Code generation == Performance gains

4. SQL --> RDD - ->SQL
a. New API makes Spark programmes more concise and easier to understand and at the same time exposes more application semantics to the engine.
Data Frames
1. There is unification across the languages and it is influenced by
python pandas and
R frameworks.
Python pandas
- sqlContext.createDataFrame(pandas)
- dataframe.toPandas()
R
- createDataFrame(sqlContext,RDataFrame)
- Collect(df)
2.Data frames are still experimental and it is available under
SAPRK-6116
3. Even it is in experimental it is also called stable component
Spark SQL Demo
1. We can use
sqlContext to work with Spark SQL.
Scala> import sqlContext.implicits._
Scala>
Implicits loaded in spark 1.3 onwards
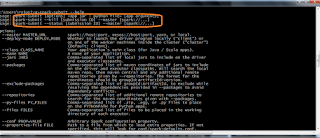
How to create class using sqlContext in Scala?
Scala> case class Company(name: String,employeeCount:Int , isPublic:Boolean)
//create list of employees data for company class
Scala> val companies = List(Company(“IBM”,25000,true), Company(“TCS”,27000,true), Company(“INFOSYS”,50000,true), Company(“Oracle”,125000,true), Company(“Cognizant”,225000,true) ,Company(“Siva Inc”,125,false))
Create a
DataFrame using
toDF method
Scala> val companiesDF = companies.toDF
or
scala> val companiesDF = sqlContext.CreateDataFrame(companies)
Display the results first 20 rows
Scala> companiesDF.show
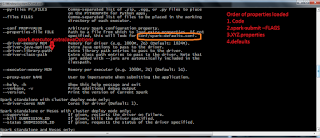
How to Load the data from the source?
Place this json file in your local system and name it as companies.json
{"employeeCount" : 10000, "isPublic": true, "name" : "Amazon"}
{"employeeCount" : 1201, "isPublic" : false, "name" : "ABC Inc"}
{"employeeCount" : 1201, "isPublic" : true, "name" : "ICIC"}
{"employeeCount" : 120000, "isPublic" : true, "name" : "NetFlix"}
{"employeeCount" : 220001, "isPublic" : true, "name" : "Spark"}
val companiesJsonDF = sqlContext.read.json(“file:///c:/spark/Companies.json”)
we can load the data using format method
val companiesJsonDF = sqlContext.read.format(“json”).load(“file:///c:/spark/Companies.json”)
Print the schema
companiesJsonDF.printSchema
unionAll
val allCompaniesDF = companiesDF.unionAll(companiesJsonDF)
we will get error, since companiesDF and companiesJsonDF schema is in different alignment order.
We can cast the required columns with the select.
Val companiesJsonIntDF = companiesJsonDF.select($”name”,$”employeeCount”.cast(“int”).as(“employeeCount”),$”isPublic”)
If we use unionAll then both Data frames will be combined.
val allCompaniesDF = companiesDF.unionAll(companiesJsonDF)
How to access union data in java
allCompaniesDF.groupBy(allCompaniesDF.col(“isPublic”)).agg(avg(“employeeCount”)).show
Filter condition using where clause
allCompaniesDF.where($”employeeCount”>100000).show
How to use in Java
allCompaniesDF.where(allCompaniesDF .col($”employeeCount”). gt 100000)).show
How to save the data
allCompaniesDF.write.json((file:///c:/spark/all.json)
we can write the same as providing format, how we have read the file same
sqlContext.write.format(“json”).save(“file:///c:/spark/Companies.json”)
How to import the ROW
Import org.apache.spark.sql.Row
How to convert data into row.
allCompaniesDF.map(company=>company(0).asInstanceOf[String])
How to retrieve column values
.foreach(println)
How to register the table to run the sql like statements.
- We can use hql also for hive tables.
allCompaniesDF.registerTempTable(“Companies”)
sql “SELECT * from Companies”
.show
Sql(“SELECT AVG(employeeCount) AS AverageEmpCount FROM Companies GROUP BY isPublic”).show
How to cache tables
Sql(“CACHE TABLE Companies”)
Spark Streaming
1. It is for streaming the data.
2. It is very popular library and it takes up the spark big data processing power and crunch up the speed.
3. It has the ability to stream GiGa byte data in sec.
4. It will steam the real time data as much fast as it can
5. It can have exactly one transformation schematics’ and failure recovery time as in matter of sec or 2 secs.
6. Due to 1 transformation the transformation output can’t be duplicated.
7. The transformation method itself will execute multiple times on failure.
Competitors
1. Apache STORM
1. Spark streaming is 40 times faster compare to STROM
2. In Storm data can be duplicated.
3. Spark is complete package we can inter mixed concepts without learning a new framework
4. STORM is true streaming framework. It will process item one by one as it arrives
5. SPARK process the incoming data as a small deterministic batch jobs. This is called micro batching.
Source of data to be stream
1. Kafka
2. Twitter
3. Flume
4. HDFS
a. Once we picked the Source then it will flow into Spark Streaming receiver. Where we have one receiver per one stream.
b. Behind the scene Streaming incoming data store into series of RDDS with specified windows of time.
c. Then each time window it will passed to spark core and it will process as normal.
d. So our stream becomes series of RDDS.
e. Here we have two points of Spark processing one is Receiver and one worker
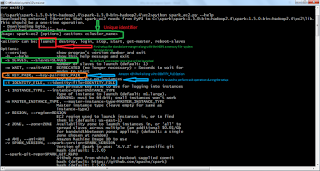
Spark Streaming DEMO
This demo will explain how to process the tweets data which is mentioned in hash tags
1. First we need to get access for twitter API.
2. Go to
https://apps.twitter.com
3. Please refer my previous posts, how to create app in twitter.
4. Provide key details in build.sbt file.
5. Write a program to retrieve the tweets data and process the same
MLlib
1. This is very complex library. Since it is having complex algorithms.
Competitors for MLlib
1. MATLAB
2. R
These are easy to use and fairly scalable.
On the other hand we are having
3. mahout and
4. GraphLab
These are more scalable and cost of use.
It was Started by MATLABS and driven by ML stack
It was a three form approach to make machine learning easy and scalable
ML Optimizer and MLI were used for machine learning pipe lines and algorithm development.
MLlib was the production implementation , that came from ML Optimizer and MLI
Spark MLlib implementation as assumed most of this stack, with mllib has original based RDD algorithms reside.
And ML name space contains high level pipe line API built on top of Data Frames. Which has taken from ML Optimizer
org.apache.spark.mllib
org.apache.spark.ml
These ML pipelines officially introduced into the Spark 1.2 as attempt to simplified machine learning.
In machine learning flow and loading the data , extracting features , training the data and testing the data.
1. Algorithms
1. Classification
2. Regression
3. Collaborative Filtering
4. Clustering
5. Dimensional Reduction
2. Feature Extraction and Transformation
3. Uses of these algorithms
1. SPAM filtering
2. FRUD Alert
3. Recommendation
4. Determine the information on clusters
5. Speech Recognition
Graphx
1. It is a library that brings table structure into grapgh like structure. Like social networking.
2. It is used for data parallel and Graph parallel
3. GraphX works RDD behind the scene. Just drawing the data in graph optimized data structure.
4. The execution run through this parallel pattern for each node computation depends on each of it’s neighbours.
5. This focus on graph specialization with some impressive performance gain.
Competitors
1. Try to run graphs on Hadoop is very complex.
2. Apache GIRAPH is another competitor but it is slow compare to Graphx while running the page rank algorithm
3. Graph Lab is 33% slower than Graphx
What kind of things we can do using GrpahX?
1. Web itself is joint graph
2. Algorithm for website rendering.(google and Wikipedia)
3. Social network data analysis using Social Graphs available.
4. Graphs available for product valuation in websites like amazon and NETFLIX
5. We can use our technological power to advance science to research generic analysis

1. Data will be referred as vertex with vertex id vertex Type
2. Again Vertex id referred as Long
 Edge will be described with vertex Id type of along with edge type
Edge will be described with vertex Id type of along with edge type

Then we will have Vertex and Edge, then we can build graph like below.
1. Graph(VType,EType)
2. Graph(RDD[Vertex],RDD[Edge])
Edge Triplet-
Grapghx will expose through object known as EdgeTriplet and it is having all the information about each connection
This will provide us on Graph complete view more reasonable understanding.
Thank you very much for viewing this post.